This article is a study note for Just Enough English Grammar to Illustrate.
NOUNS
FORM OF ENGLISH NOUNS
Types of Nouns
| Type | Example | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| Proper | Susan | specific |
| Common | school, suntan lotion | general |
| Concrete | hamburger, suntan lotion | senses |
| Abstract | love | out of senses |
| Collective | family | groups |
| Compound | suntan lotion | more words |
Singular and Plural Nouns
+ s
s,x,z,sh + es
f or fe to v,ve + es
y—i + es
Common Noun Suffixes
Adding -er indicates the person who is carrying out an action.
Adding -ance indicates the fact or state of carrying out an action.
Adding -ness indicates a quality or state of being.
Adding -ity indicates an action or state of affairs that is
abstract.
Gender of Nouns
Masculine Nouns
Feminine Nouns
Neuter Nouns
Articles
Indefinite Articles(General):a/an (a boy/boys)
Definite Articles(Specific):the (the boy/the boys)
USES OF ENGLISH NOUNS
We conclude this chapter with a Venn diagram that summarizes how the
noun $trophy$ can be used when forming sentences.

Nouns as Subjects
A noun that names the person(s) or thing(s) about which a statement is
to be made is labeled the subject,which includes simple and compound
subjects.
Who:people
What:inanimate objects
Nouns as Subject Complements
A subject complement describes or renames the subject.
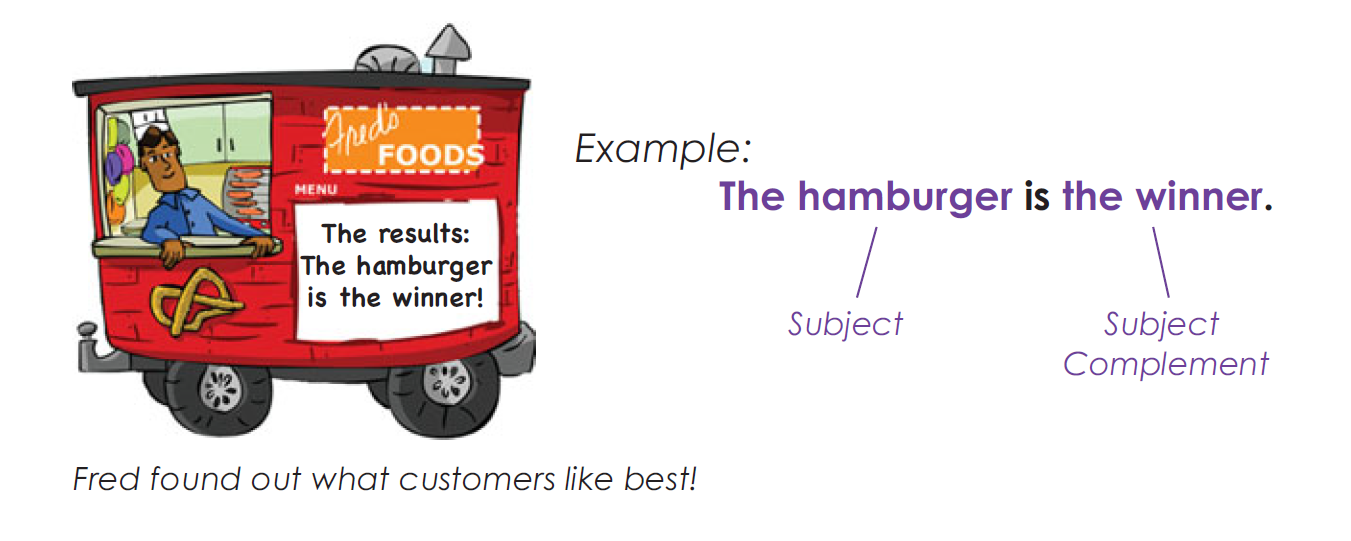
Linking verbs help to make a statement not by expressing an action,
but by serving as a link between the subject and the subject
complement.$Am, are, is, was$, and $were$ are all forms of the most commonly
used linking verb $to\quad be$.Any form of $to\quad be$, when it acts as a linking verb, can be
represented by an equals sign.
Possessive Nouns
To show relationship or ownership of a noun,add an apostrophe.
Use $of$ instead of the apostrophe, and switch the order of the
nouns.
EXAMPLES:the pool’s diving board = the diving board of the pool
What Is a Sentence?
Units are composed of different parts that we will call building
blocks.
Nouns as Direct Objects
The direct object , which need action verbs 1, is a word or
group of words that directly receives the action expressed by the verb.
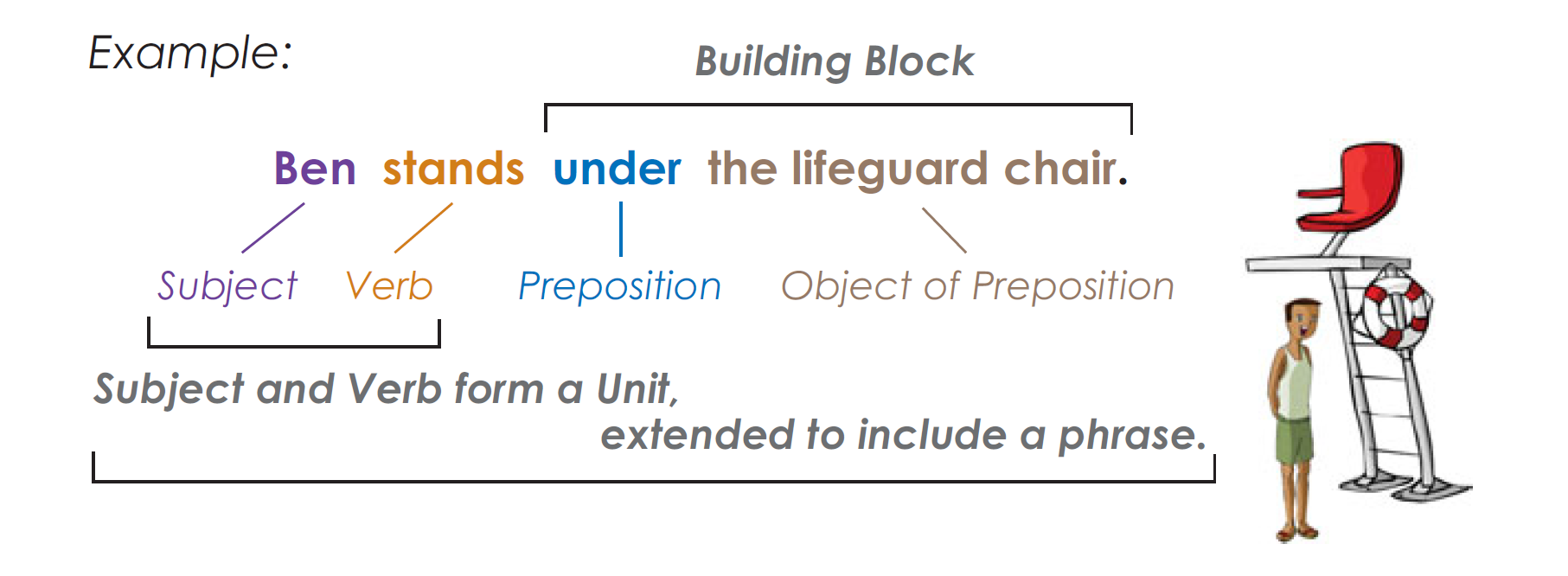
Nouns as Objects of Prepositions
A noun used after a preposition is called the object of the preposition.
ADJECTIVES
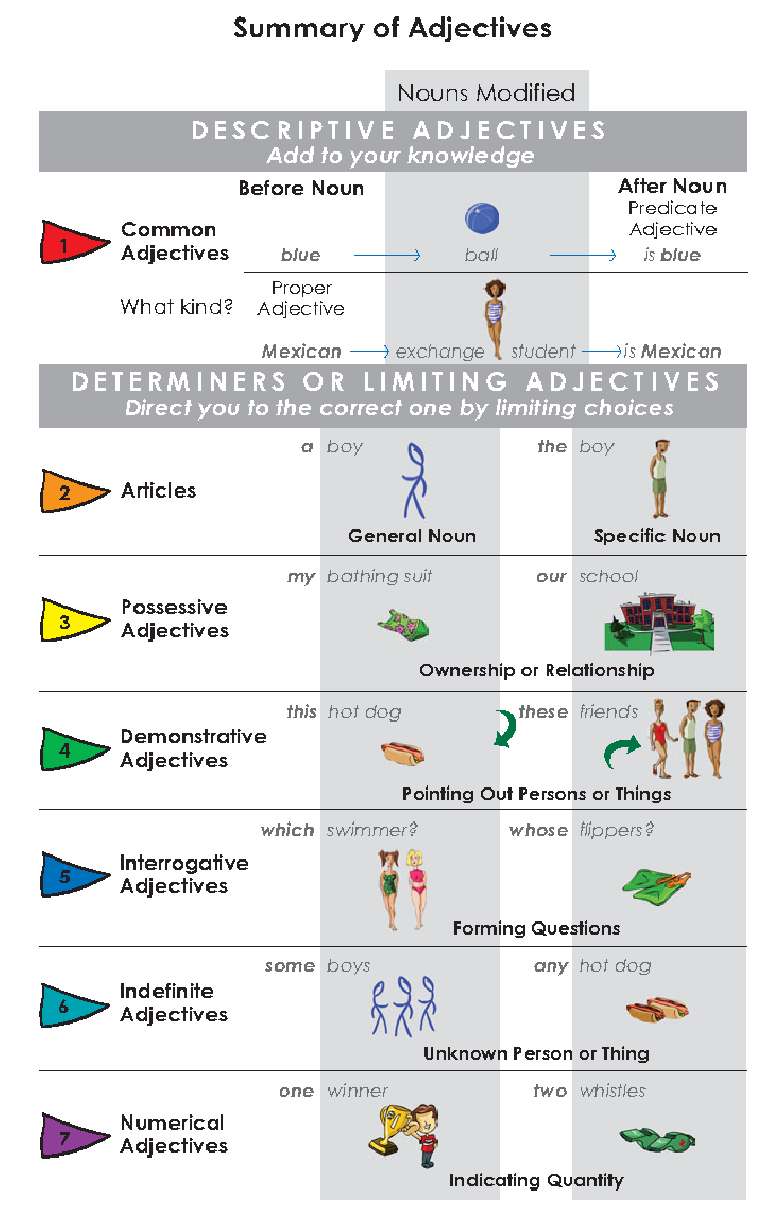
Descriptive Adjecitives
In general, common adjectives are placed before the noun they are
describing.

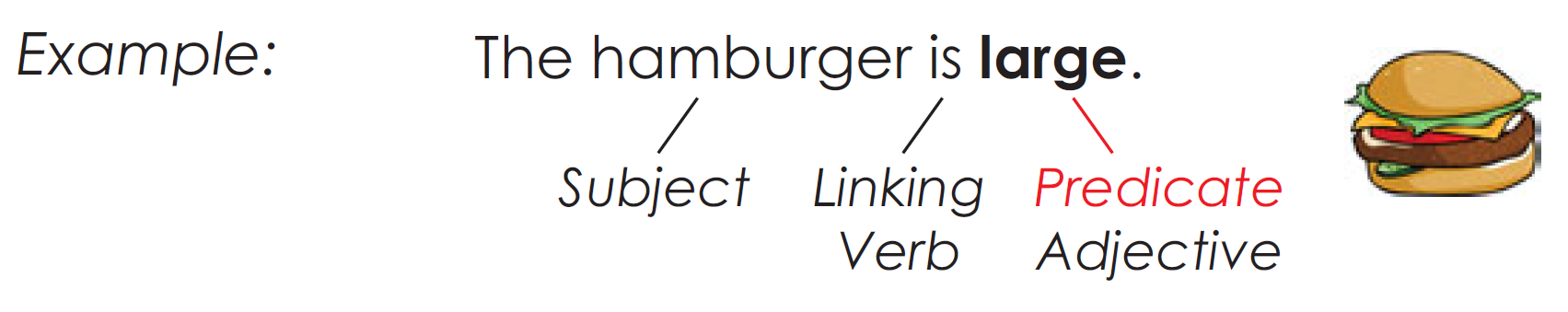
Predicate adjectives are placed after the linking verb
$to \quad be$. They always expand on the subject.
An adjective formed from a proper noun is called a proper
adjective. It is always capitalized.

Determiners or Limiting Adjectives
A determiner is placed before the noun it modifies and helps to identify
a specific noun rather than describe it.

Articles
Indefinite Articles:$A$ and $an$ refer to one of a general group.
Definite Articles:$The$ indicates that the noun (either singular or
plural) refers to someone or something in particular.
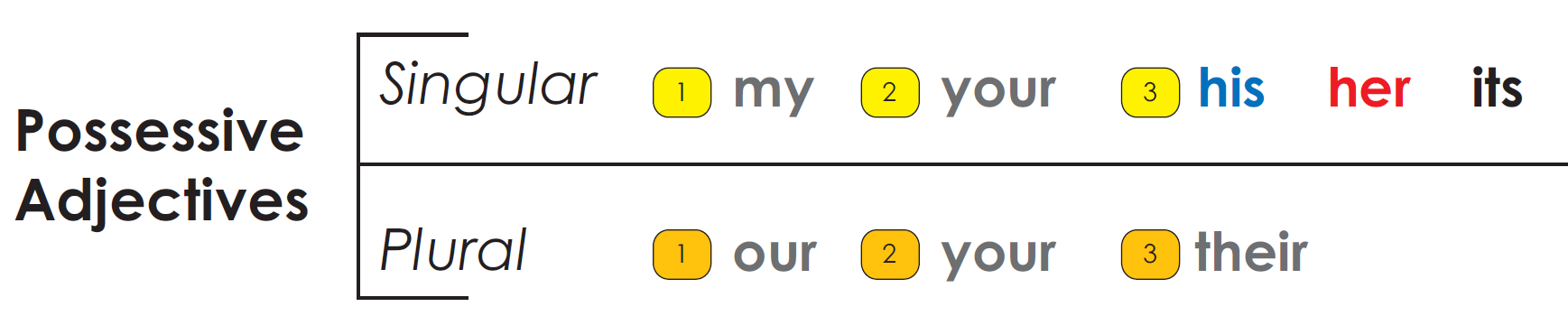
Possessive Adjectives
Possessive adjectives are derived from these $personal$ $pronouns$2
and express the idea of possession.
Demonstrative Adjectives
Demonstrative adjectives point out persons or things.This and
that are singular; these and those are
plural.
Interrogative Adjectives
The interrogative adjectives which, what, and
whose, together with the nouns they modify, are commonly used
to form questions.
Indefinite Adjectives
Indefinite adjectives indicate nonspecific persons or
things.Some, each, any, many,
and several are examples of indefinite adjectives.
Numerical Adjectives
Numerical adjectives indicate quantity by stating a fixed number of
people or things.
Suffixes and Origin of Adjectives
Suffixes are attached to a root word to form the adjective. These
adjectives originate from other types of words, such as nouns or verbs.
PRONOUNS
We conclude this chapter with a Venn diagram that summarizes how the
pronoun $trophy$ can be used when forming sentences.
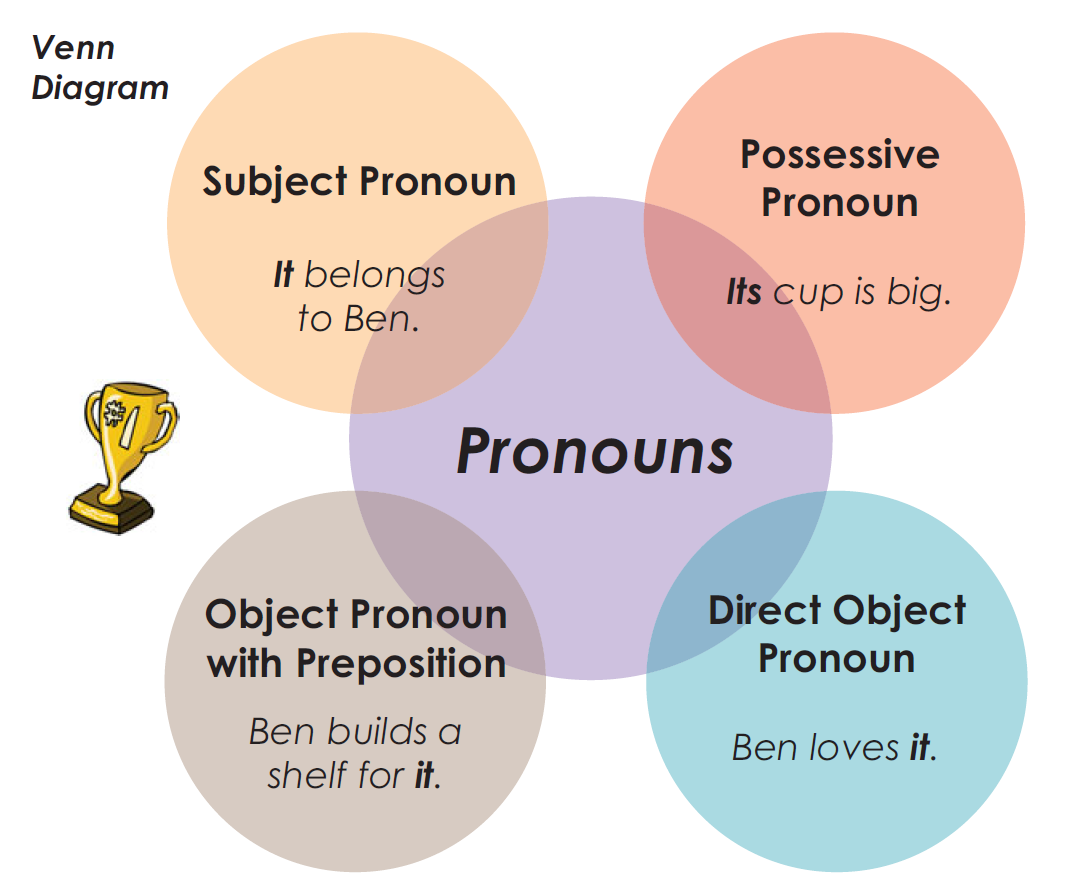
What Information Do Pronouns Give?
Uses of Pronouns
Common Uses of Pronouns:
To replace people, places, or things: he, it
To introduce a question: Who, What
To point to a specific person, place, or thing: this
(one), that (one), these, and thoseTo refer to unnamed, nonspecific people or
things: Singular: each, somebody, something, or anything.Plural:
both, several, few, or many.
Personal Pronouns
$I$, $you$, $he$, $she$, $it$, $we$, $they$
Grammar Person of Pronouns
Every personal pronoun is classified by whether it is first, second, or
third person.
First person pronoun: I, We(Plural)
Second person pronoun: You, You(Plural)
Third person pronoun: He, She, It, They(Plural)
Possessive Pronouns
$Mine$, $yours$, $his$, $hers$, $its$, $ours$, $yours$, and $theirs$
Number of Pronouns
Singular:$I$, $you$, $he$, $she$, $it$
Plural:$we$, $you$, $they$
Gender of Pronouns
Gender does not differentiate the pronouns “I,” “you,” “we,” and
“they.”
Three genders differentiate the third-person singular pronouns :
Masculine Pronoun:he
Feminine Pronoun: she
Neuter Pronoun: it
We say “generally” here because pronouns do not always follow these
simple rules: Animals are classified as male or female, and sometimes
inanimate objects (such as ships and boats) are referred to as she.
What Jobs Can Pronouns Do?
The roles pronouns can play divide them into three distinct groups:
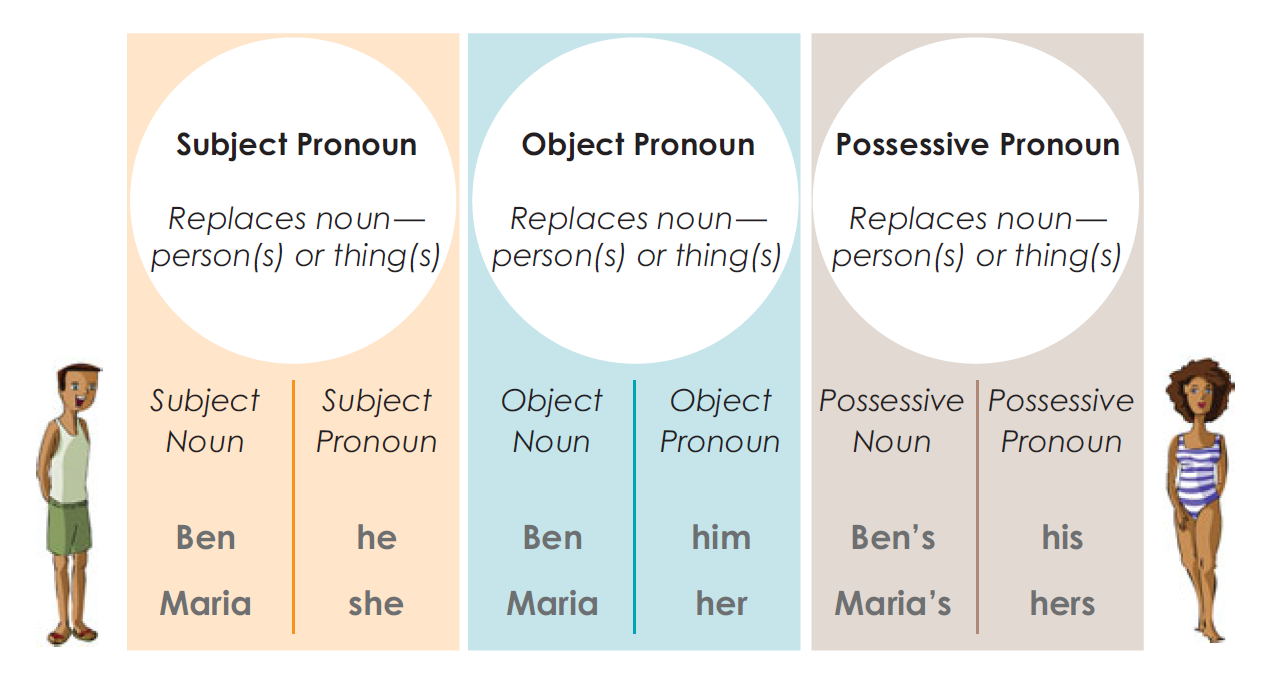
Pronouns as Subjects and Pronouns as Direct Objects
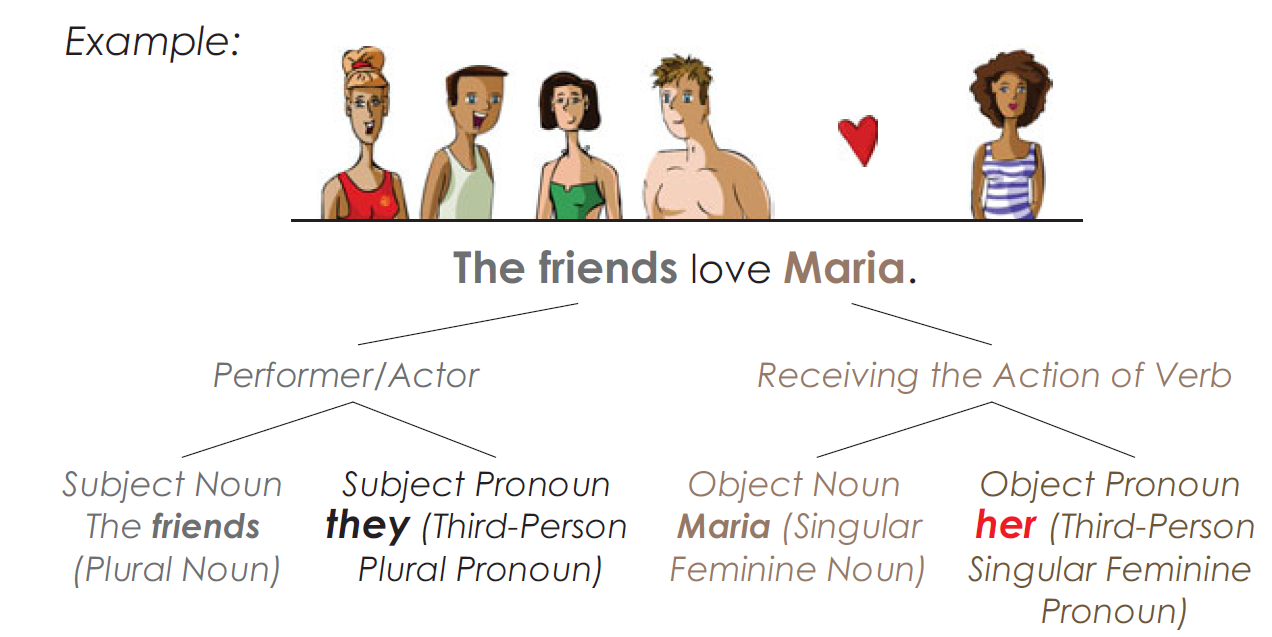
Pronouns as Objects of Prepositions
Object pronouns can be used to complete a prepositional phrase.
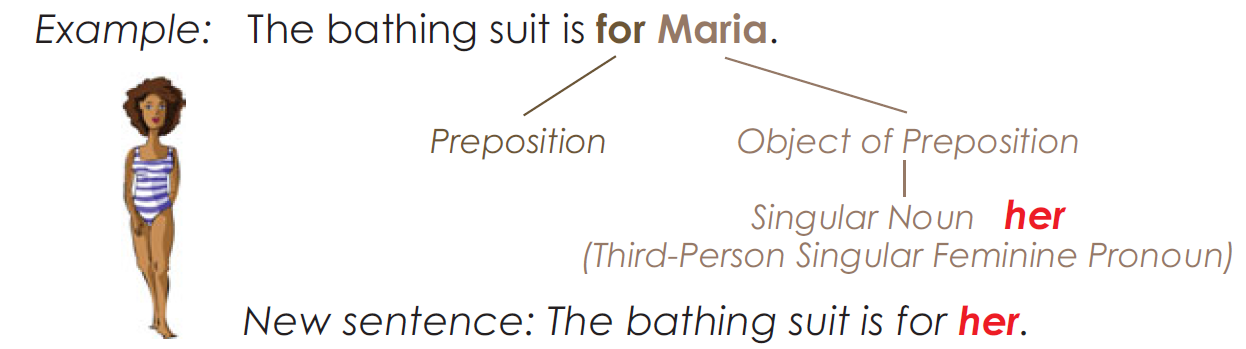
Possessive Pronouns

Pronouns as Question Words
Question Words Asking About the Subject: $Who$, $What$
Question Words Asking About the Object: $Whom$. $What$ plays a
double role(subject or object).Question Word Asking About a Possessive Noun: $Whose$
VERBS
This chapter takes a close look at all the jobs verbs can perform.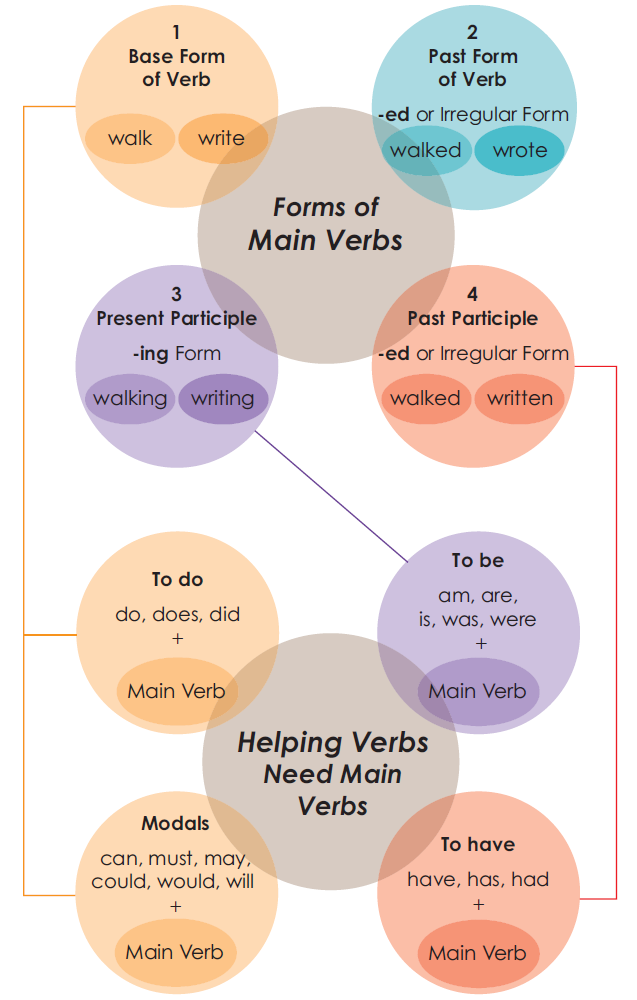
FORM OF ENGLISH VERBS
Verb Families
The infinitive form consists of the word “to” plus the base form of a
verb.
Types of Verbs
Action Verbs: Action verbs express the action, often physical
action, that the subject does.(to eat)Non-Action Verbs: Non-action verbs tell about states of mind or
senses.(to think, to look, and to understand.)Linking Verbs: Linking verbs convey a state of being. They
link the subject of a sentence with a word that renames or describes
the subject.(to be,to appear, to become, to feel, to grow,
to look, and to taste.)Helping Verbs: Main verb may need a helper to express its full
meaning: [to be am, are, is, was, were]{.underline} [to do do, does,
did]{.underline} [to have have, has, ha]{.underline}d [Could, would,
and must]{.underline}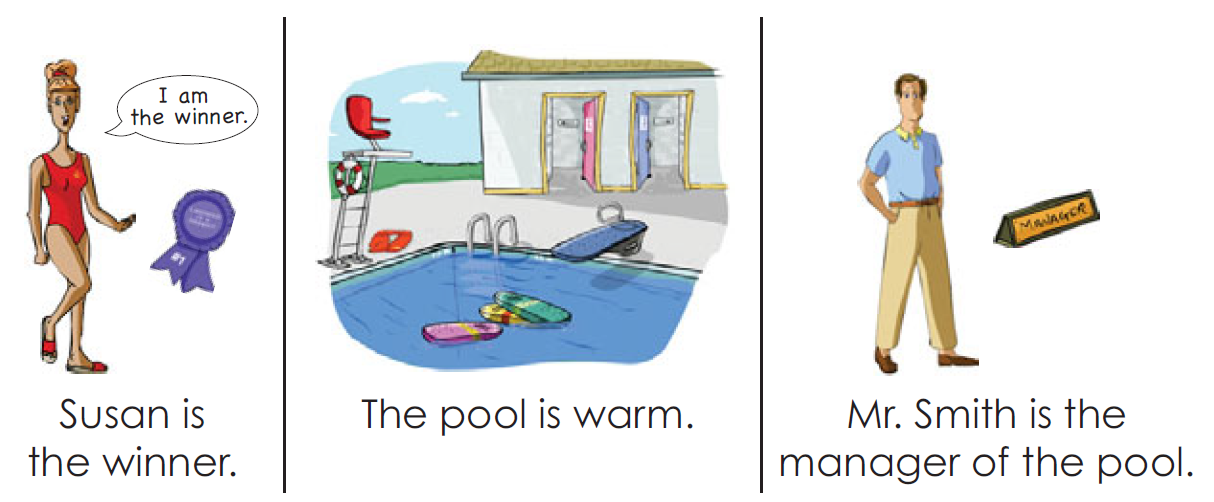
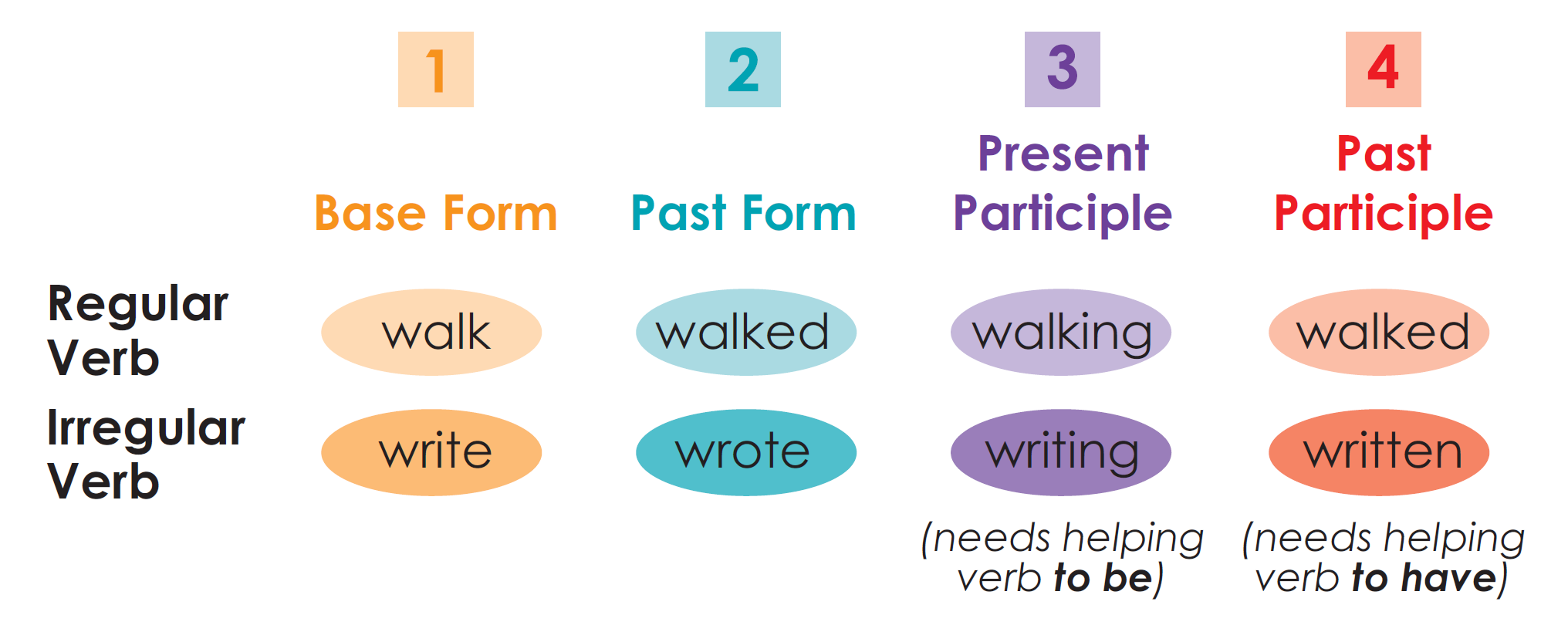
Regular and Irregular Verbs
Verbs change in form. Based on how they change, verbs are divided into
two groups.
The Four Principal Parts
USES OF ENGLISH VERBS
Tense
Now:Present Tense,Present Continuous
Yesterday:Past Tense,Present Perfect
Tomorrow: Future Tense
Modals: Special Helping Verbs
Some common modals are $can$, $could$, $may$, $might$, $must$, $should$,
and $would$
Modals as helping verbs express:
possibility or necessity
ability or permission
polite requests
Linking and Non-Action Verbs as Main Verbs
When looking at the definitions of verb tenses, the terms $action$ and
$condition$ appear often.They indicate $conditions$ showing what the
subject is, or is like.It can be used as a main verb, just like other
verbs.
Linking Verbs: $be$
Non-Action Verbs: $have$
Verbs in Questions and Statements
There are two main kinds of questions in English:
Questions beginning with a main or helping verb(direct questions) A
form of “to do,” in either present or past tense, must be used to
form questions, unless the main verb is the linking verb “to be.”Questions beginning with a main or helping verb(information
question) Like direct questions, most questions that begin with a
question marker, such as what, why, when, and how, follow inverted
word order. When “who” or “what” replaces the subject to form a
question, regular word order applies.
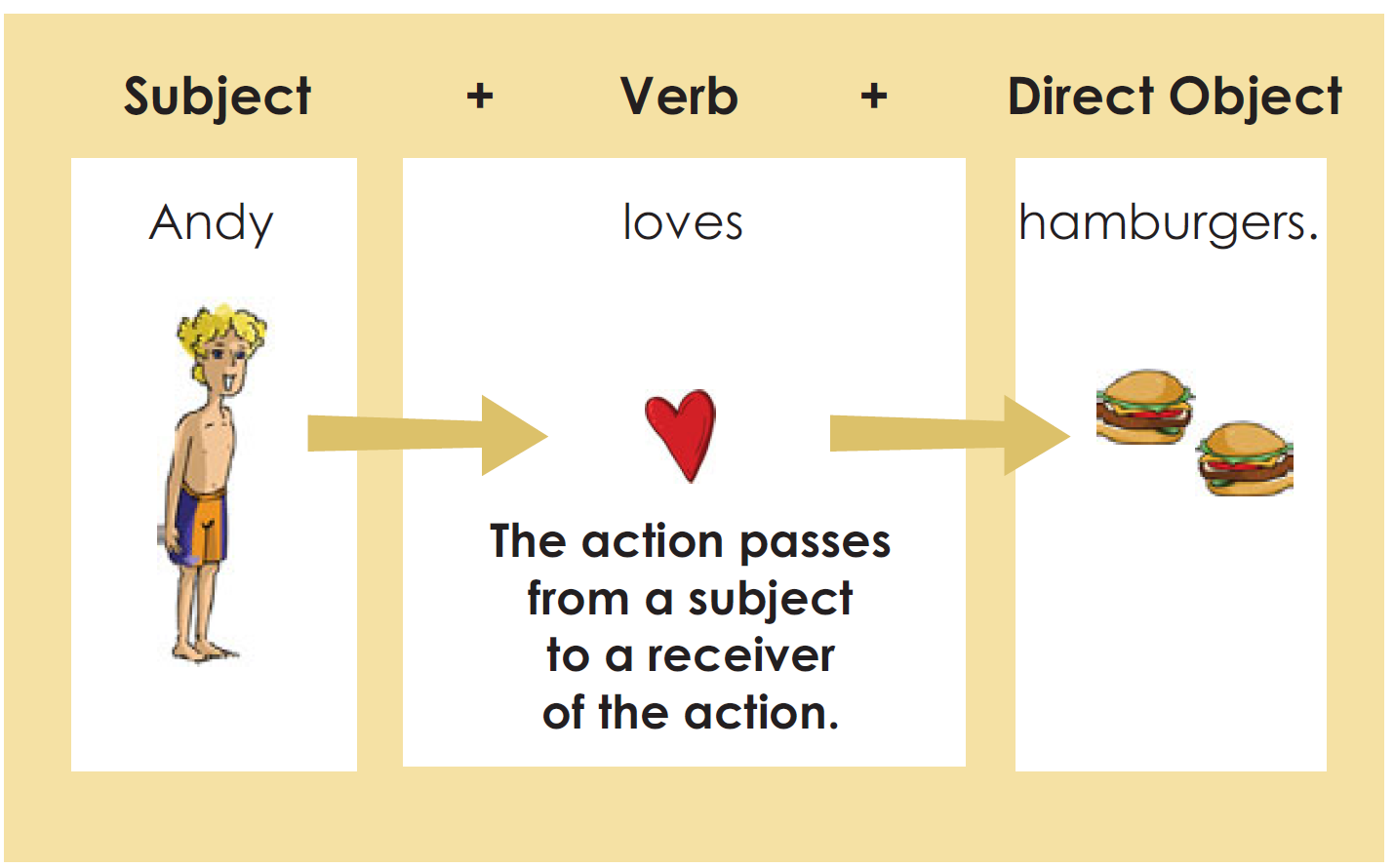
Verbs with Direct Objects
The direct object names the receiver of an action. It completes the
meaning of the sentence.
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
- Transitive Verbs
A transitive verb has a direct object. A verb is transitive when an
object is necessary to complete its meaning in the sentence. The
action of the verb is transferred to the object.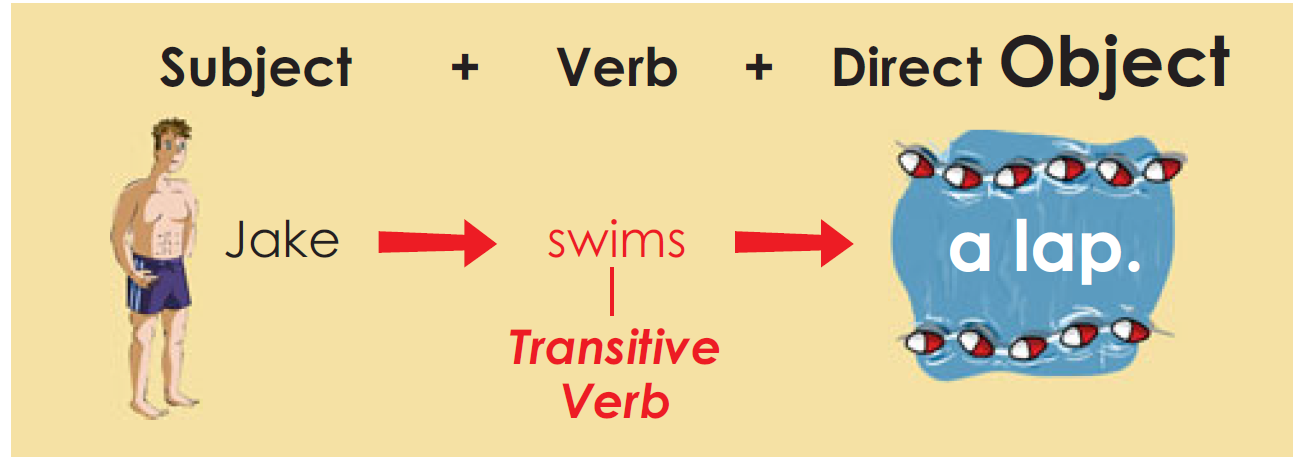
- Intransitive Verbs
An intransitive verb does not have a direct object. When an object
is not needed to complete its meaning, the verb is intransitive.
Verbs Expressing Commands
A sentence that gives a command or make a request is called an
imperative sentence.
ADVERBS
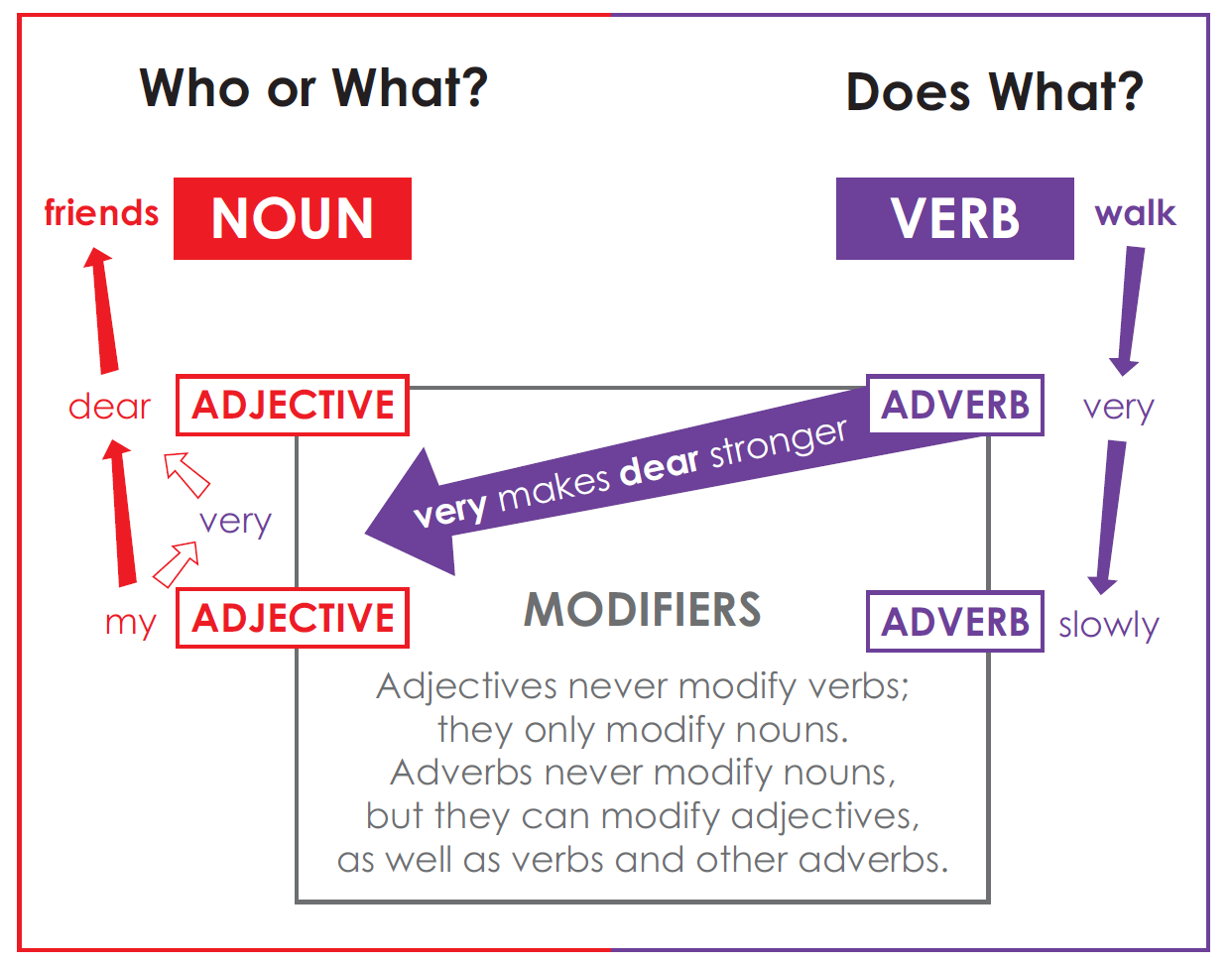
What Is an Adverb?
Adverbs act as modifiers. The prefix “ad-“ in the word adverb
means “to,” “toward,” or “in addition to.” An adverb is a word that is
used with a verb to expand its meaning.
Five Groups of Adverbs That Modify Verbs
Adverbs of Time: early, today, now, yesterday, before, soon, and
tomorrow.Adverbs of Location: above, inside, here, there, and everywhere
Adverbs of Manner:loudly, carefully, well, quickly, and slowly
Adverbs of Degree:completely, nearly, too, almost, very, and fully
Adverbs of Frequency:always, often, sometimes, seldom, and never
Most
Adverbs Used to Form Questions
“When,” “where,” and “how”(interrogative adverbs) are used to form
questions.
When Adjectives Become Adverbs
Most adjectives become adverbs by adding the suffix -ly. Some examples
of adverbs that cannot be identified as adverbs by looking at a suffix
are seldom, again, soon, almost, fast, and now.
When Adverbs Modify Other Adverbs
The meaning of an adverb can be made stronger by adding a second adverb.
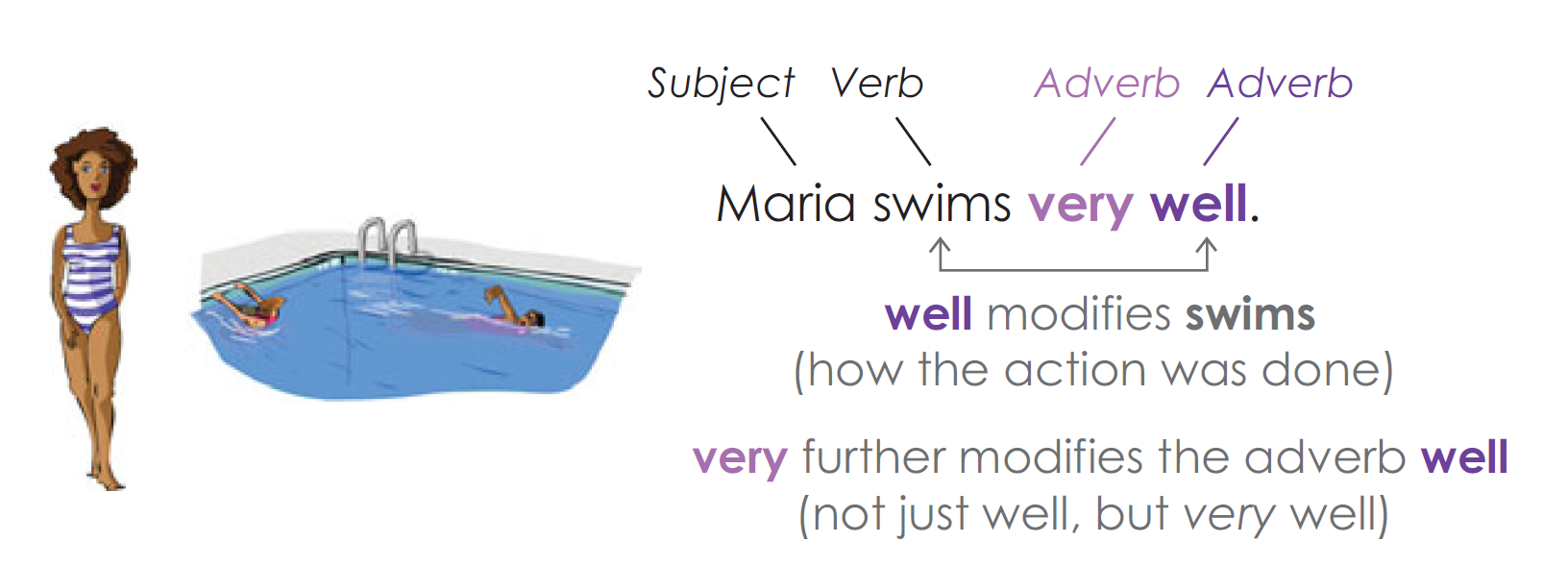
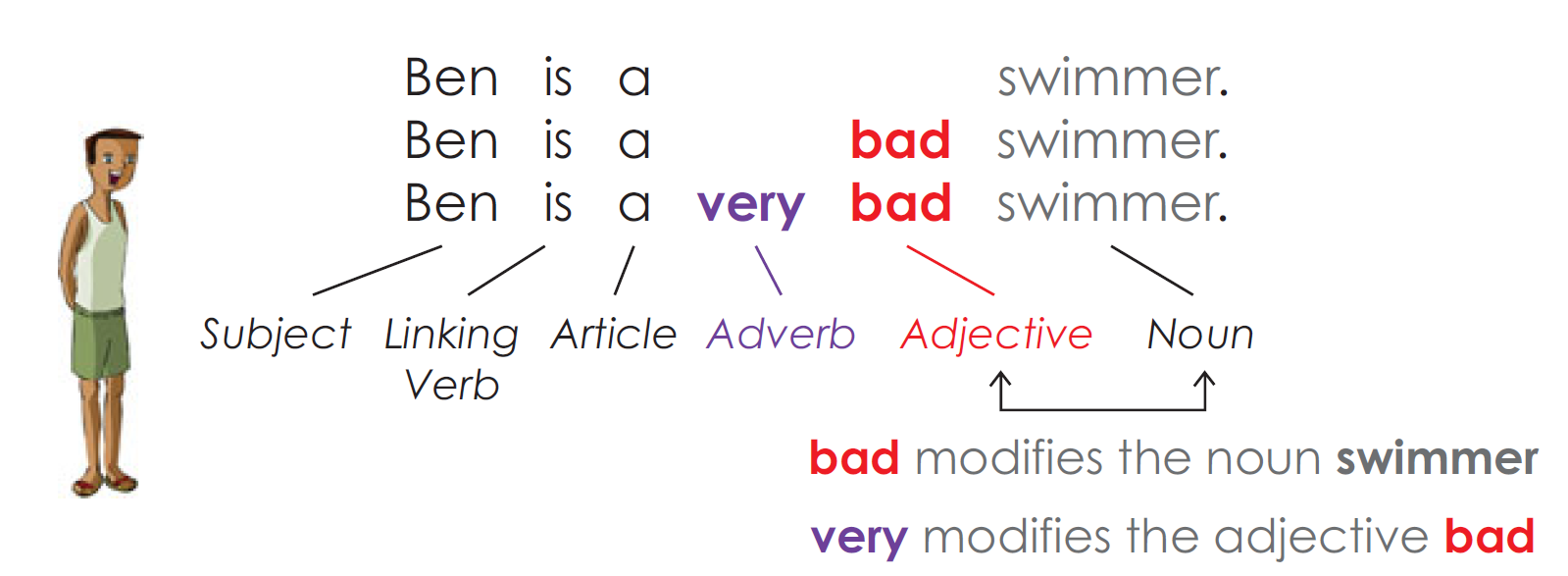
When Adverbs Modify Adjectives
Adverbs of degree can modify both other adverbs and adjectives.
PREPOSITIONS
What Is a Preposition?
A preposition is a word or group of words that is placed before a noun
or a pronoun to show a relationship in a sentence.
Frequently Used Prepositions

Prepositional Phrases with Nouns and Pronouns
A preposition and the object of the preposition form a prepositional
phrase.
A pronoun used as the object of a preposition must be an object pronoun;
it cannot be a subject pronoun.
Extended Units with Direct Objects and Objects of a Preposition
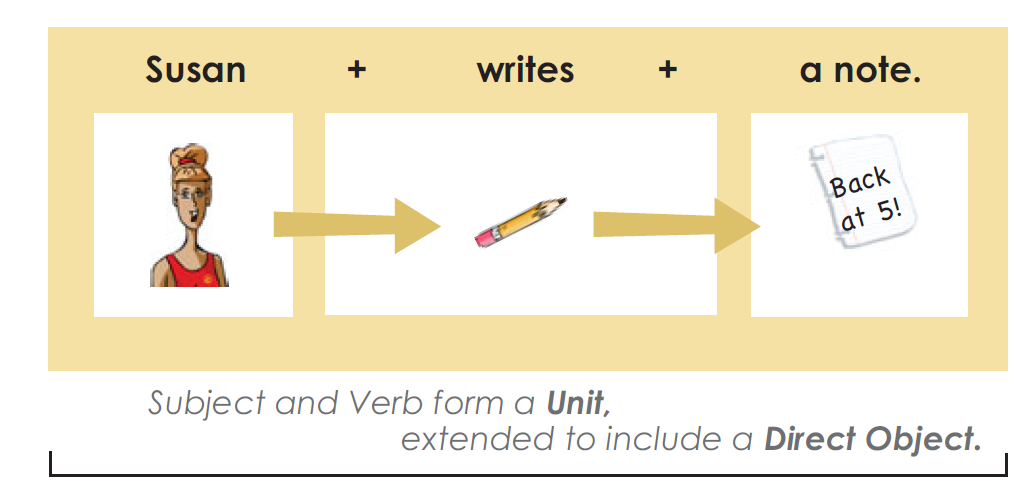
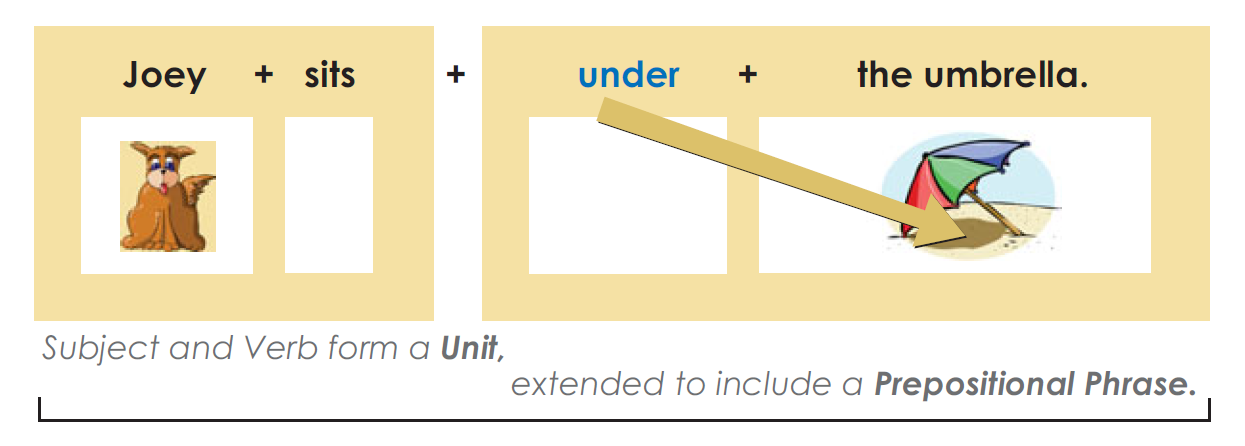
Some Words Are Both Prepositions and Adverbs
Some words can be used as prepositions when they have an object, but
they can also be used as adverbs when they do not have an object.

CONJUCTIONS
What Is a Conjunction?
A conjunction joins words or a group of words of the same
type.
$and$ expresses addition
$or$ expresses a choice
$but$ expresses contrast
Joining Words
Examples:
- Maria wears her green or pink bikini almost every day
during the summer.
Joining Phrases
Examples:
The hula girl performed for Jake last week and for Maria
this week.Is the lifesaver near the pool or in the locker room?
Joining Sentences
Examples:
We went to the pool, and the Miller family went to the
parade.All the friends came, but Maria was not there.
INTERJECTIONS
An interjection(exclamation) expresses strong emotion or surprise; it
functions independently within a sentence.
Common interjections include wow, well, hey, bravo, and
oh.
Vocabulary
formal exposure 正式接触
The parts of speech 词性
spark 火花
biography 传记
locker room 衣帽间
towel 毛巾
life preserver 救生设备
suntan (晒黑) lotion
air mattress 空气垫
goggles 护目镜
ladder 梯子
concession stand 小卖部
Overview 概述
inanimate 无生命的
Masculine 男性的
Feminine 女性的
bull 公牛
cow 母牛
affirmative 肯定的,同意的;
action-packed 内容丰富有趣的;令人激动的
coordinate v. 协调,配合 n. 坐标;配套服装;adj.
地位相当的,同等重要的;ordinate n. 纵坐标 v. 授某人以圣职;命令
parade 游行
comma 逗号
proficiency n. 熟练,精通
undergraduate 大学本科生
prestigious adj. 有威望的,有声望的
assignment n.
作业,任务;(工作等的)分配,指派;(财产、权利的)转让prestigious assignments 重要职位